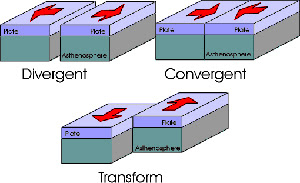
GUIDELINES- Writing, Speaking, Listening
GUIDELINE- The Writing Process
Study Skills
Free Help with Homework
Managing Back-to-School Anxiety
*When studying for Science Tests/Quizzes, it's always good to use a combination of these resources:
- Read and study all your class notes
- Study worksheets given (highlight them too)
- Look at Videos/links on my blog (YouTube helps too)
- Look at the different websites on the Websites and Resources for Science folder on my blog, including Ducksters.com (for Fact information)
- Make Flashcards of important Vocabulary terms
- Practice on Quizlet website (Flash cards, Match games)
- Take practice Quizzes (on my blog, under Quizzes folder)
- BrainPop videos + Review Quizzes (and take notes on the videos)
- Read Summary Notes (if given) or Study Guides, including the Study packet that covers all 3 years of Science
- Practice past 8th Grade Science State Exams (link on my blog)
- Practice on IXL + Khan Academy
- Study Textbook (look at Chapter Tests, Vocabulary words)
- Make a study group with friends (you can test each other on different topics)
Here's a quick video on BrainPop with tips on how to study and prepare for a test --> BrainPop- Test Preparation
- Make a study group with friends (you can test each other on different topics)
Here's a quick video on BrainPop with tips on how to study and prepare for a test --> BrainPop- Test Preparation